Clouds fill the skies above us and are part of our every day lives but often go unnoticed. However, there are some clouds that are so rare you must be very lucky to see them in your lifetime. This is a list of the top 10 most rarest cloud formations (in no particular order) that for those lucky enough to see them, were caught on camera.
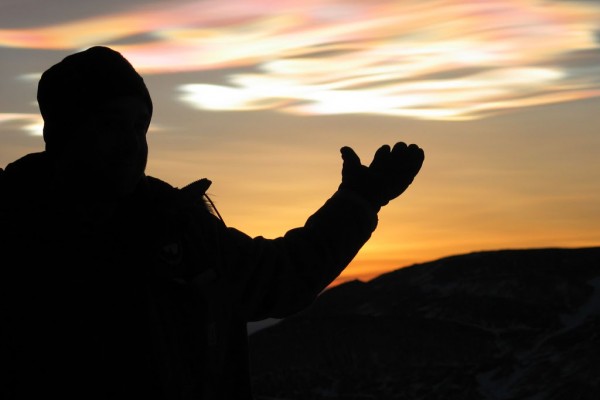
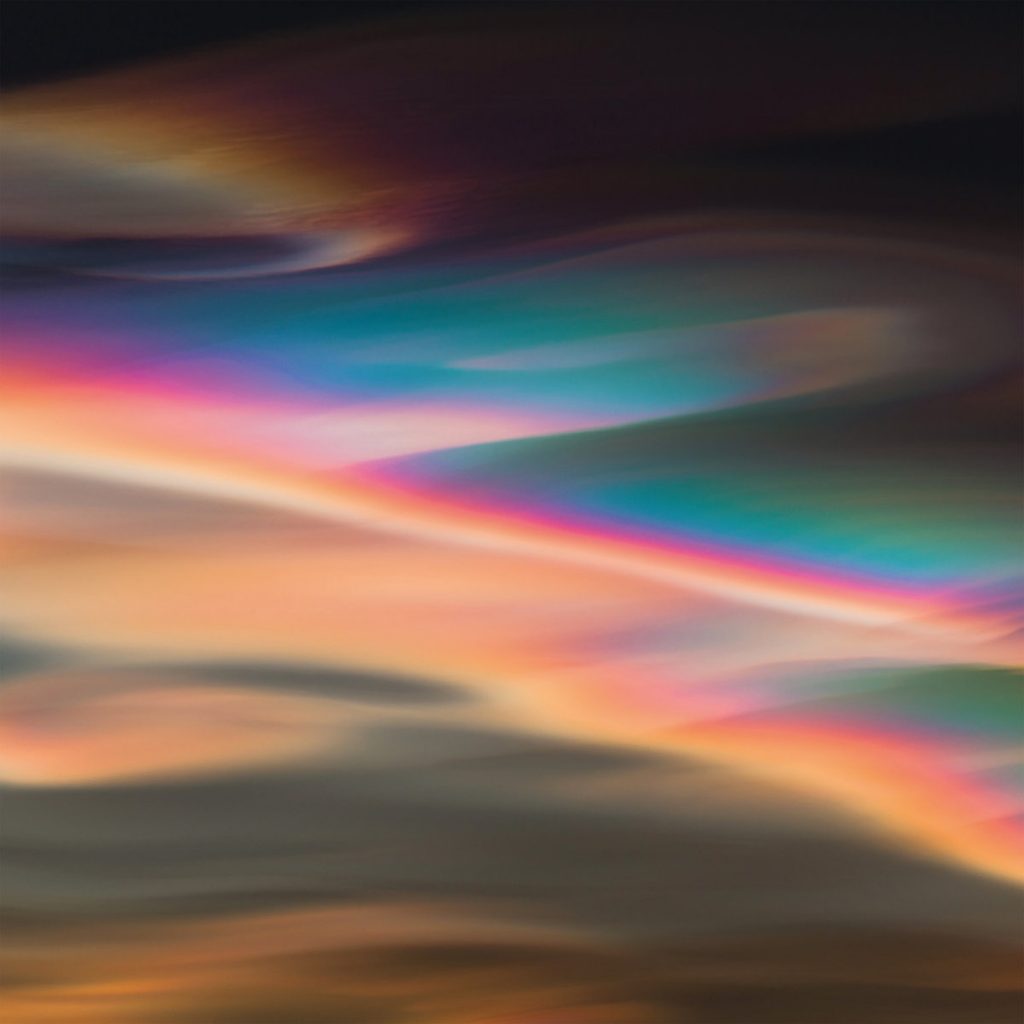
1. Nacreous Clouds
These rare clouds, sometimes called mother-of-pearl clouds, are 15 – 25km (9 -16 miles) high in the stratosphere and well above tropospheric clouds. They have iridescent colours but are higher and much rarer than ordinary iridescent clouds. They are seen mostly but not exclusively in polar regions and in winter at high latitudes, Scandinavia, Alaska, Northern Canada. Lower level iridescent clouds can be seen anywhere.

Nacreous clouds shine brightly in high altitude sunlight up to two hours after ground level sunset or before dawn. Their unbelievably bright iridescent colours and slow movement relative to any lower clouds make them an unmistakable and unforgettable sight.

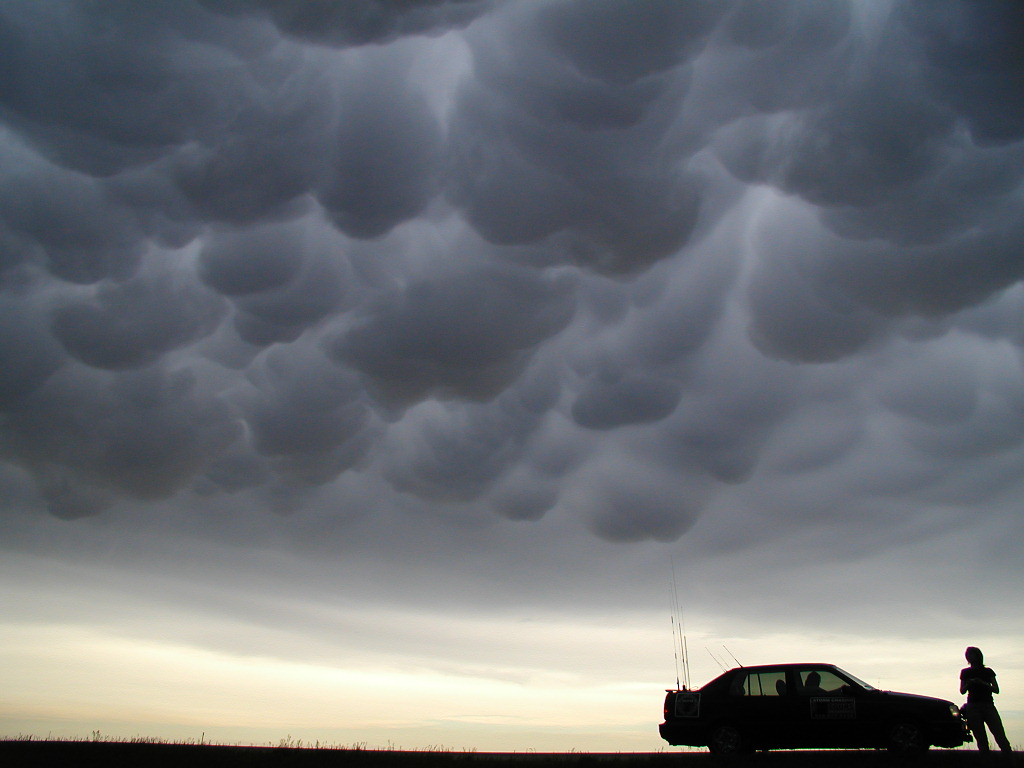
2. Mammatus Clouds
Mammatus Clouds are pouch-like cloud structures and a rare example of clouds in sinking air. Sometimes very ominous in appearance, mammatus clouds are harmless and do not mean that a tornado is about to form – a commonly held misconception. In fact, mammatus are usually seen after the worst of a thunderstorm has passed.
3. Altocumulus Castelanus
Also known as jellyfish clouds due to their jellyfish-like appearance. These formed around 17,000 ft due to when the rush of moist air comes from the Gulf Stream and gets trapped between layers of dry air. The top of the cloud rises into a jellyfish shape and long tentacles known as “trailing virga” form from rain drops that have evaporated.
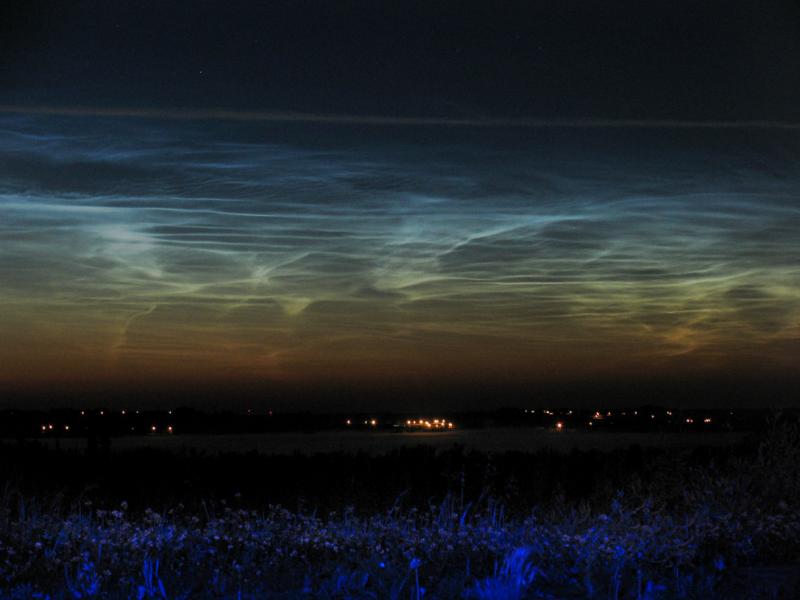
4. Noctilucent Clouds
Noctilucent Clouds or Polar Mesopheric Clouds: This is supremely rare cloud formation that occurs out on the verge of space between 82km to 102 km from the earth’s surface. Noctilucent clouds appear to be luminous yet they reflect the sunlight from the other side of the earth at night, giving them a glowing appearance.


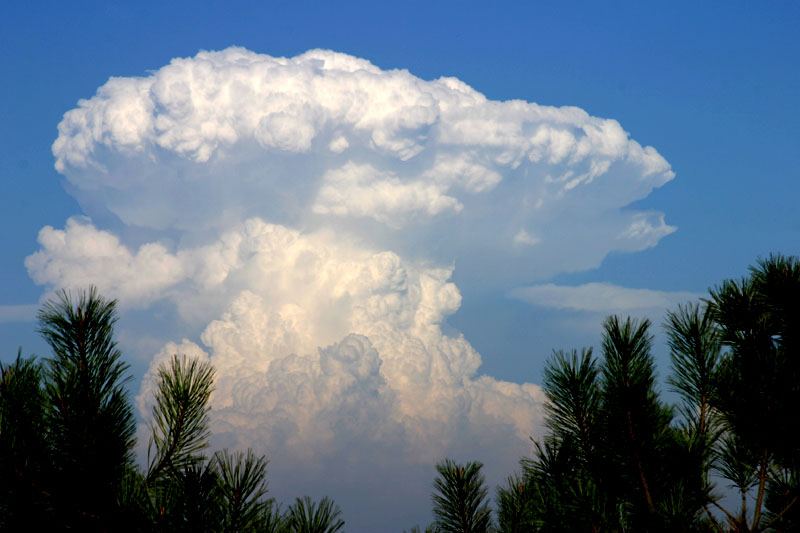
5. Mushroom Clouds
A mushroom cloud is a distinctive mushroom-shaped cloud of smoke, condensed water vapour, or debris resulting from a very large explosion. They are most commonly associated with nuclear explosions, but any sufficiently large blast will produce the same sort of effect. Volcano eruptions and impact events can produce natural mushroom clouds. Mushroom clouds as a result of the sudden formation of a large mass of hot low-density gases near the ground creating a Rayleigh-Taylor instability. The mass of gas rises rapidly, resulting in turbulent vortices curling downward around its edges and drawing up a column of additional smoke and debris in the centre to form its “stem”. The mass of gas eventually reaches an altitude where it is no longer less dense than the surrounding air and disperses, the debris drawn upward from the ground scattering and drifting back down.
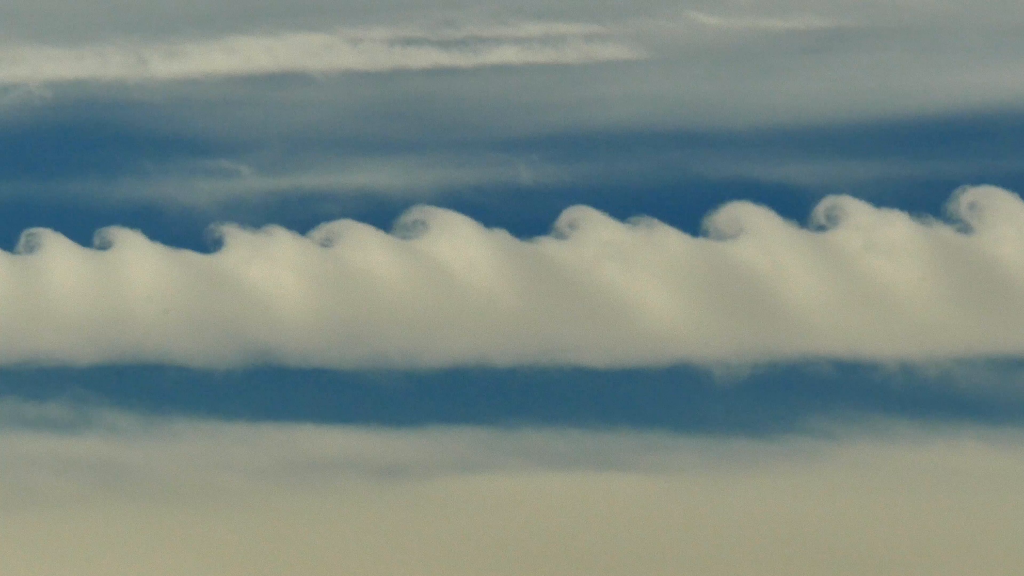
6. Cirrus Kelvin-Helmholtz
Appearing as a slender, horizontal spiral of cloud, cirrus Kelvin-Helmholtz is one of the most distinctive cloud formations. However, it tends to dissipate only a minute or two after forming and, as a result, is rarely observed. Average height is around 16,500 ft.
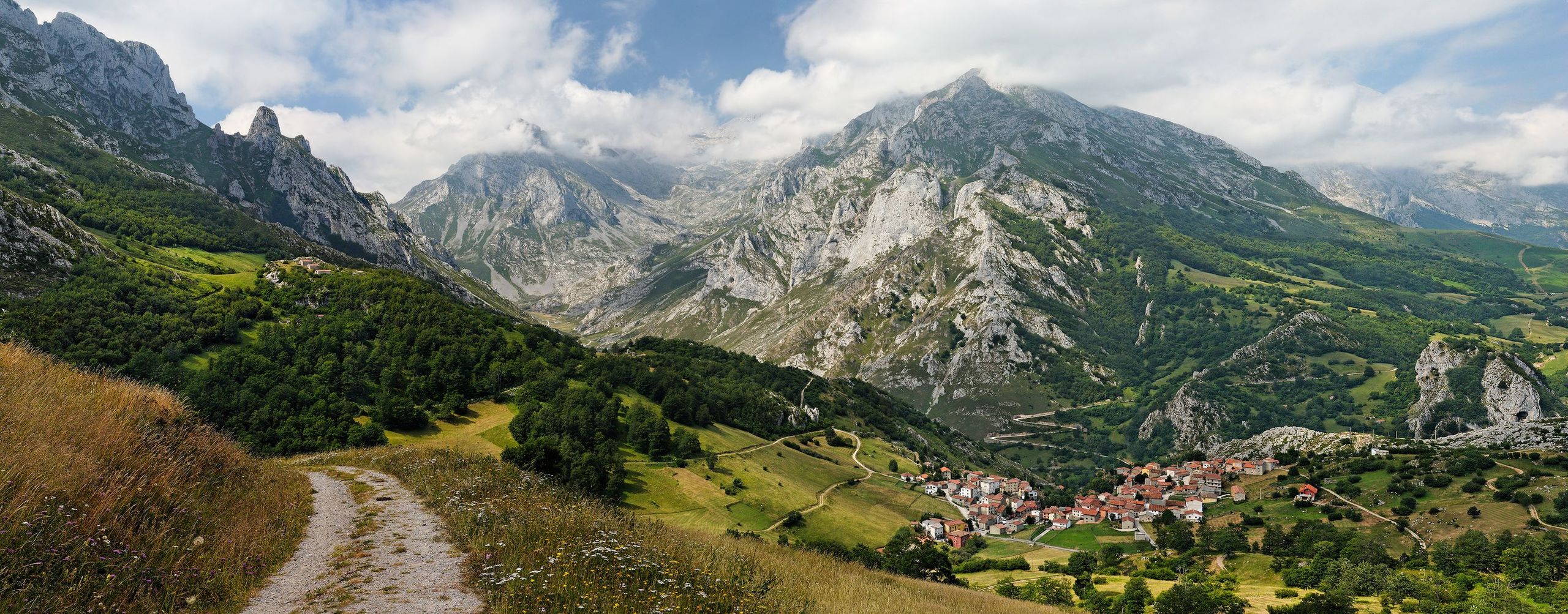
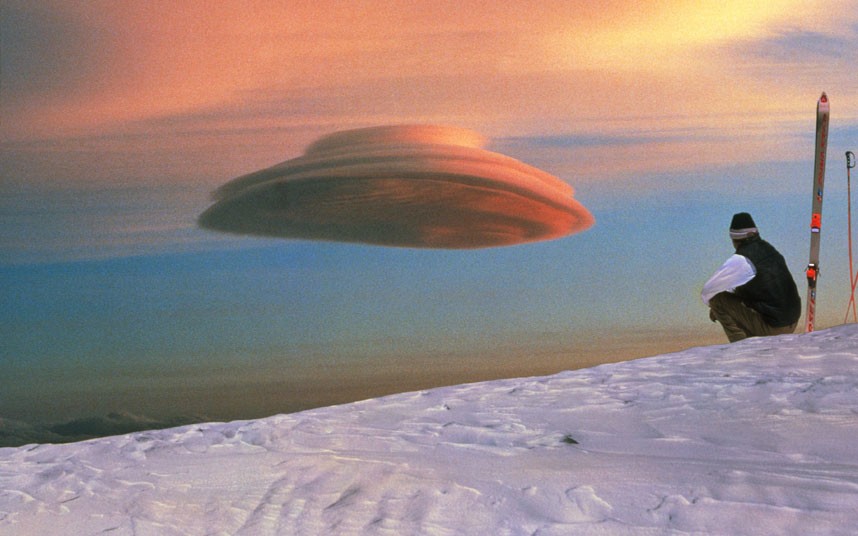
7. Lenticular Clouds
Lenticular Clouds, technically known as altocumulus standing lenticularis, are stationary lens-shaped clouds that form at high altitudes, normally aligned at right-angles to the wind direction. Where stable moist air flows over a mountain or a range of mountains, a series of large-scale standing waves may form on the downwind side. Lenticular clouds sometimes form at the crests of these waves. Under certain conditions, long strings of lenticular clouds can form, creating a formation known as a wave cloud. Lenticular clouds are popular with UFO believers because they often look like flying saucers. The lens-shaped clouds form at high altitude and are usually formed when moist air passes over a mountain range and is heated adiabatically (that is, without any transference of heat energy) as it descends. The cloud pattern depends upon the wind speed and the shape of the mountains. A constant wind may produce clouds which are stable and remain virtually stationary in the sky for long periods.

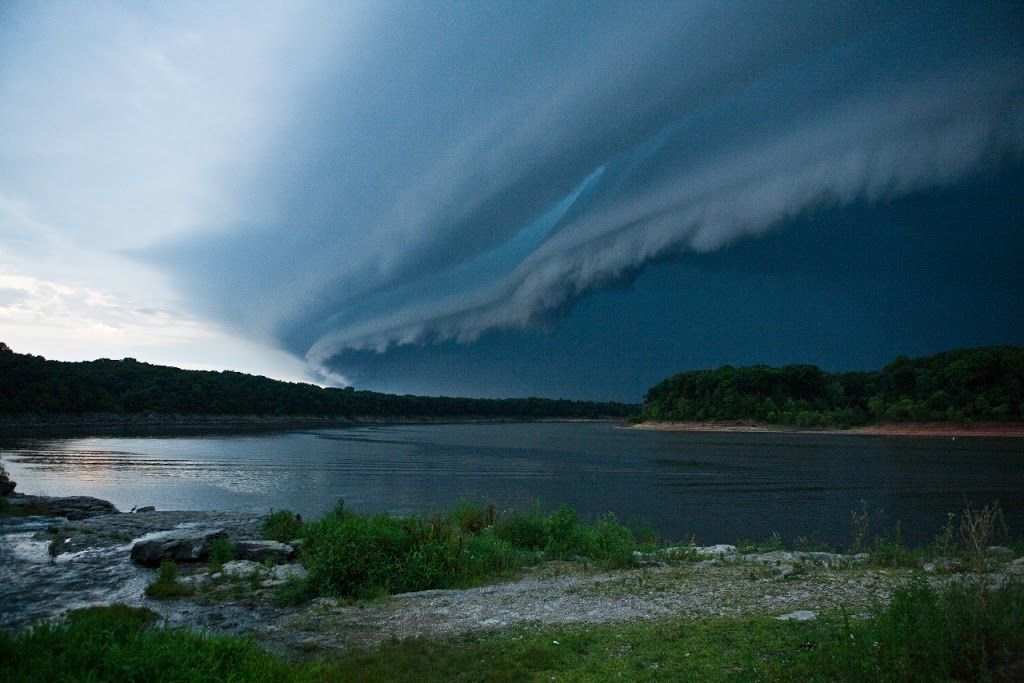
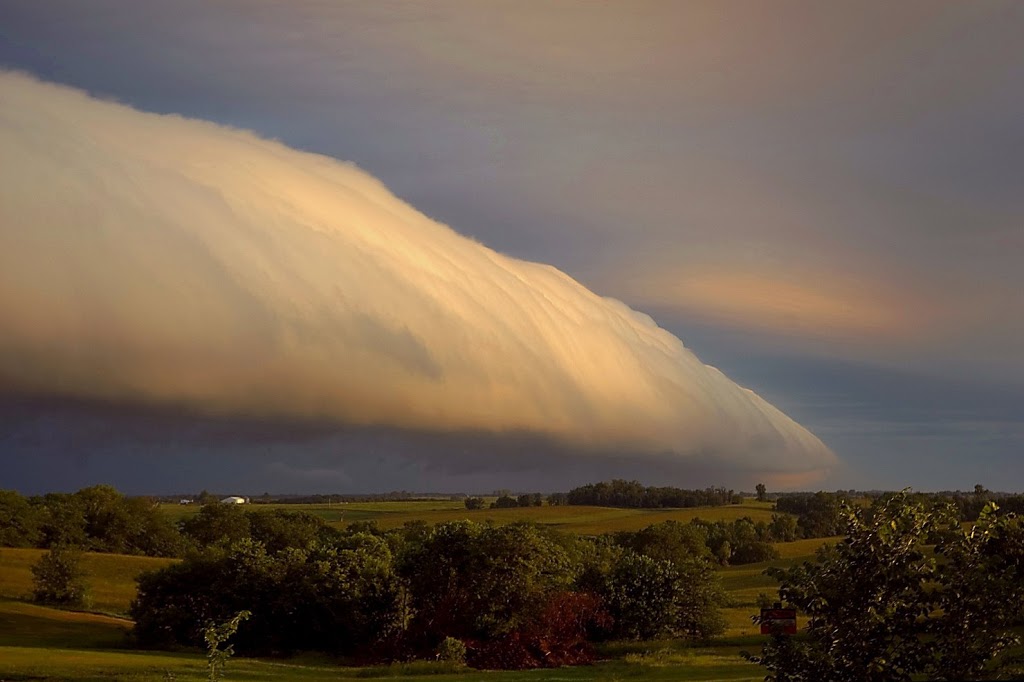
8. Roll Clouds and Morning Glory Clouds
A roll cloud is a low, horizontal tube-shaped arcus cloud associated with a thunderstorm gust front, or sometimes a cold front. Roll clouds can also be a sign of possible microburst activity. Cool air sinking air from a storm cloud’s downdraft spreads out across the surface with the leading edge called a gust front. This outflow undercuts warm air being drawn into the storm’s updraft. As the cool air lifts the warm moist air water condenses creating cloud, which often rolls with the different winds above and below (wind shear). Roll clouds are basically shelf clouds without attachment to a thunderstorm.

Morning Glory cloud is a rare meteorological phenomenon occasionally observed in different locations around the world. The southern part of Northern Australia’s Gulf of Carpentaria is the only known location where it can be predicted and observed on a more or less regular basis due to the configuration of land and sea in the area. The settlement of Burketown attracts glider pilots intent on riding this phenomenon.
9. Shelf Clouds
A shelf cloud is a low, horizontal wedge-shaped arcus cloud, associated with a thunderstorm gust front (or occasionally with a cold front, even in the absence of thunderstorms). Unlike a roll cloud, a shelf cloud is attached to the base of the parent cloud above it (usually a thunderstorm). Rising cloud motion often can be seen in the leading (outer) part of the shelf cloud, while the underside often appears turbulent, boiling, and wind-torn.
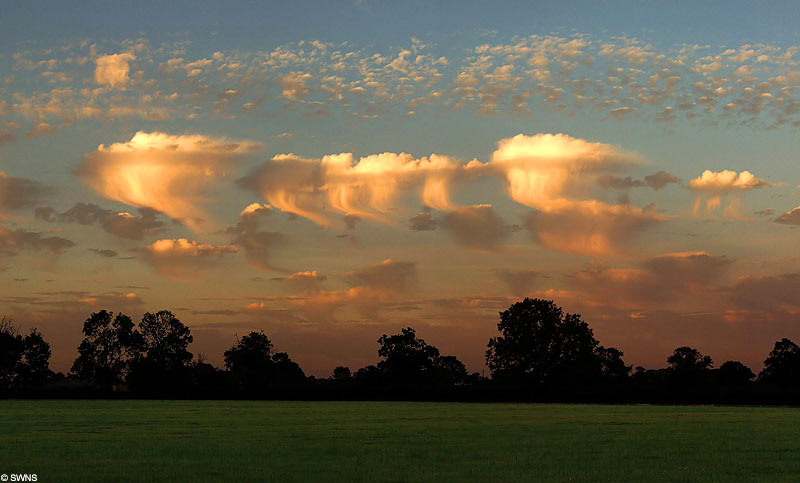
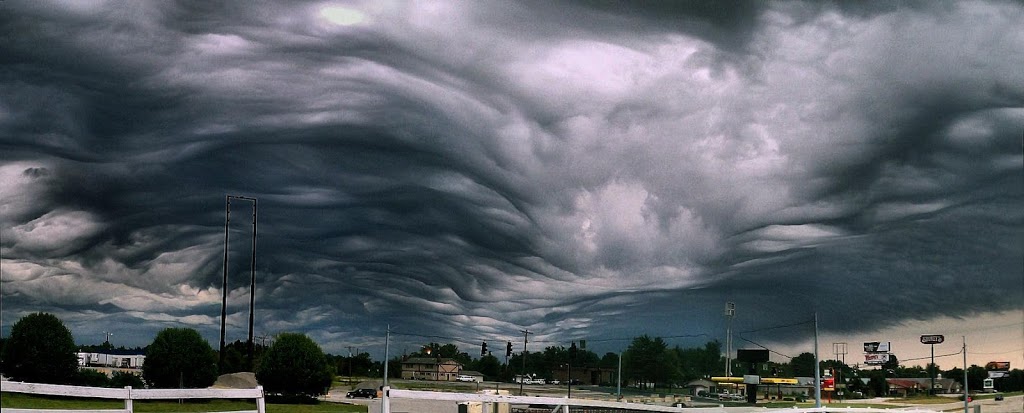
10. Undulatus Asperatus Clouds
Undulatus asperatus is a cloud formation, proposed in 2009 as a separate cloud classification by the founder of the
Cloud Appreciation Society. If successful it will be the first cloud formation added since cirrus intortus in 1951 to the International Cloud Atlas of the World Meteorological Organisation. The name translates approximately as “roughened or agitated waves”.