Creative design is the process of transforming ideas into functional, visual, or physical outcomes, and in modern production, that process is inseparable from machines that enable precision and control. Across manufacturing and product development, the majority of commercial products now rely on digitally controlled equipment at multiple stages of design and execution. This dependence is not about replacing imagination. It is about making creativity reliable.
As products become more complex and expectations rise around quality, movement, and durability, designers need systems that translate intent into measurable action. Machines no longer wait at the end of the process. They influence form, motion, and feasibility from the very first design decision. This article explains why machines shape modern creative design, how that shift happened, which technologies matter most, and how creativity and engineering now work together.
Why Does Creative Design Depend More on Machines Today?
Creative design relies more on machines today because modern products must meet aesthetic, functional, and production requirements simultaneously. In simple terms, machines allow creative ideas to exist within real-world constraints instead of breaking under them. Designers no longer create in isolation. They work inside systems where tolerances, materials, motion, and repeatability matter. A surface must align. A mechanism must move smoothly. A component must perform the same way thousands of times. Machines convert creative intent into controlled parameters such as speed, force, position, and finish. That conversion is what allows creativity to scale.
How Did Creative Design Work Before Advanced Machines?
Creative design historically relied on manual craftsmanship and iterative adjustment. Designers created forms first and adapted them later to match the limits of tools and human skill. This approach worked well for custom or artistic work. It struggled when precision, speed, or volume became important. Manual processes introduce variation. Each build becomes slightly different, even in skilled hands. The shift occurred when digital design met digitally controlled machines. From that point on, creativity could be tested, measured, and reproduced rather than guessed.
What Types of Machines Shape Modern Creative Design?
Machines that shape modern creative design are systems that turn digital intent into physical or functional output. They influence what can be designed, how quickly it can evolve, and how reliably it can be produced. Most real products rely on multiple machine categories. A design may be prototyped additively, refined subtractively, formed automatically, and tuned through motion systems. The most influential categories include CNC machines, industrial 3D printers, automated fabrication equipment, and precision motion control technology.
CNC Machines
CNC machines are computer-controlled systems that remove material to create precise geometry. In creative design, CNC machining turns digital models into exact physical forms. The working principle is programmed control of position, speed, and depth. That control enables tight tolerances and clean finishes. CNC machines support metals, plastics, and composites. They are essential when fit, alignment, and repeatability matter.
Industrial 3D Printers
Industrial 3D printers are additive machines that build parts layer by layer from digital files. They enable creative design by allowing fast iteration and complex internal geometry. Additive manufacturing enables rapid testing of ideas. Designers can evaluate ergonomics, proportion, and assembly without committing to tooling. This speed changes how creative decisions are made.
Automated Fabrication Machines
Automated fabrication machines are systems that bend, form, or assemble materials with minimal manual input. They support creative design by making scalability predictable. Their working principle is controlled application of force and sequence. That predictability allows designers to push complexity without sacrificing consistency. Automation connects creative ambition with production reality.
Precision Motion Control Systems
Motion control is the technology that governs how systems move, stop, and hold position. In creative design, motion defines how a product feels to the user. Smoothness, responsiveness, and accuracy are not aesthetic details. They are functional qualities. Design teams often begin by understanding what is motion control because movement behavior shapes the entire design system. Motion requirements determine geometry, materials, and even surface finish. Servo motor behavior, servo mechanisms, and control architecture all influence whether a design feels refined or crude.

How Do Machines Influence Design Decisions Before Anything Is Built?
Machines influence design decisions by defining feasibility early. When designers understand what machines can and cannot do, concepts evolve inside realistic boundaries. Motion-driven designs force early decisions about acceleration, torque, and stability. Surface-driven designs force early decisions about finish and preparation. These constraints are not obstacles. They prevent late redesigns and wasted effort. Designs that acknowledge machines early are more likely to survive the transition to production.
What Are the Main Benefits of Machine-Driven Creative Design?
Machine-driven creative design offers several core advantages that reshape how ideas become products. These advantages appear when machines are integrated early rather than added at the end. There are six advantages listed below.
- Enhance precision by converting digital intent into controlled output
- Expand design freedom through reliable geometry and motion profiles
- Accelerate iteration by shortening prototype cycles
- Improve consistency by eliminating manual variation
- Enable scalability from prototype to production
- Reduce long-term risk by validating feasibility early
Together, these benefits allow creativity to function at an industrial scale.
What Are the Limitations of Relying Too Much on Machines in Design?
Relying too heavily on machines introduces trade-offs that must be carefully managed. Machines enforce discipline, but they can also narrow exploration if misused. Rigid workflows can limit spontaneity. Technical complexity can slow teams without experience. There are five disadvantages listed below.
- Increase upfront costs for equipment and integration
- Limit spontaneity when workflows are overly rigid
- Require technical expertise to avoid configuration errors
- Constrain materials to machine-compatible options
- Introduce dependency on uptime and maintenance
Balanced teams use machines as guides, not dictators.
How Do Designers and Engineers Collaborate Around Machines?
Designers and engineers collaborate around machines by sharing measurable goals. Digital models become the common language. Designers define experience and intent. Engineers define parameters and limits. Machines act as neutral arbiters. They reveal what works and what does not. This collaboration prevents creative ideas from collapsing late in development.
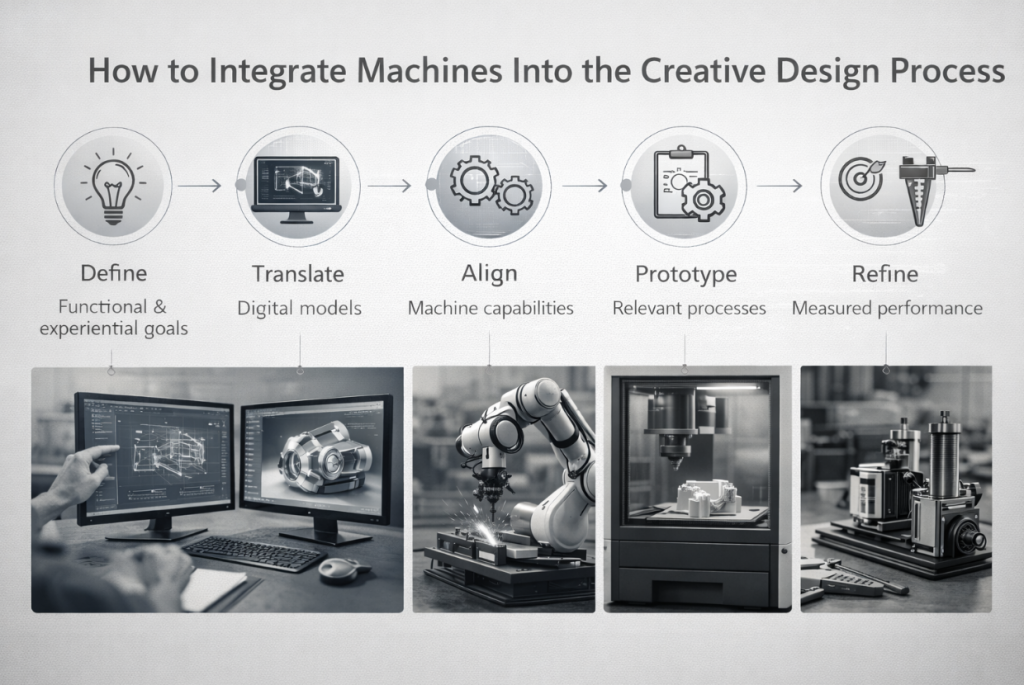
How to Integrate Machines Into the Creative Design Process
Integrating machines into creative design works best when manufacturing realities are considered from the start. The process follows a precise sequence. There are five steps involved.
- Define the concept with functional and experiential goals
- Translate ideas into digital models
- Align designs with machine capabilities
- Prototype using relevant processes
- Refine based on measured performance
Early validation protects creative intent.
How to Choose the Right Machine for a Design Concept
The right machine is chosen by matching design requirements to technical capability. The goal is suitability, not maximum sophistication. Material, geometry, tolerance, and motion all matter. Motion-driven products must consider servo motor types and control behavior early. Choosing correctly preserves creativity instead of limiting it.
How Do Machines Change the Economics of Creative Design?
Machines change design economics by reducing waste and shortening iteration cycles. An upfront investment shifts costs forward but lowers long-term expenses. Repeatability reduces rework. Automation reduces manual labor dependency. Creativity becomes more predictable financially.
Why Does Surface Preparation Matter for Design Validation?
Surface preparation affects how parts fit, bond, and perform over time. Contaminated surfaces distort test results. Laser cleaning is a surface preparation process that removes rust, coatings, and residues using controlled laser energy. It preserves base material integrity. In design validation, using laser cleaning machines allows teams to test finishes and assemblies under realistic conditions. That improves reliability and reduces rework.
Is Machine-Driven Design More Expensive?
Machine-driven design involves higher upfront costs but lower lifecycle costs. Industrial systems range from tens of thousands to several hundred thousand USD. There are five cost factors.
- Machine type and accuracy class
- Material compatibility
- Design complexity
- Production volume
- Post-processing requirements
Cost efficiency improves with scale.
Which Industries Rely Most on Machine-Enabled Creative Design?
Machine-enabled creative design is essential in industries where precision and consistency matter. These industries rely on machines to meet expectations. There are six major industries.
- Consumer products
- Architecture and interiors
- Automotive
- Fitness and wellness equipment
- Commercial equipment
- Sustainable energy products
In each case, creativity depends on controlled execution.
Can Creativity Exist Without Machines Anymore?
Creativity can exist without machines, but it cannot scale without them. Machines turn imagination into repeatable experience. They do not replace creativity. They make it usable.
Conclusion
Creative design relies more on machines because they convert ideas into reliable reality. From motion control to surface preparation, modern products are shaped by what can be measured and repeated. When designers understand machines, creativity becomes stronger, not weaker. Machines are not the opposite of design. They are what allow design to survive the real world.





